Most performance issues I’ve seen in JavaScript apps weren’t caused by React, Node or bad code.
There were caused by waiting on the database
That’s the gap Redis was built to fill.
Redis is not that thing we add later when things get slow. Redis is a tool you design for when you care about speed, scale and real-time behavior.
What Redis actually gives
Redis keeps data in memory that means
- No disk I/O
- No Complex query planner
- No locking chaos
Just
- Predictable latency
- sub-millisecond reads
- Simple mental model
It’s fast not because it’s cleaver, because it does less.
Why Redis fits JavaScript well
- NodeJS is event driven, Redis is also event-driven
- NodeJS avoids blocking threads, Redis avoids locking.
This is why Redis shows up in:
- Session handling
- rate limiting
- real-time dashboards
- chat systems
- leaderboards
Not as an experiment but as infrastructure
Cases
-
While working on APIs ask below questions:
- Does the endpoint return mostly common data for many users?
- Does it hit the database every time?
- Does it get called more often than it changes?
If yes, that endpoint wants Redis
-
Do you store:
- user sessions?
- OTPs?
- Verification tokens?
- temporary flags?
If you’re putting those in a database:
You’re using a screwdriver where a hammer exists
-
Have you ever write below query
ORDER BY score DESC LIMIT 10You just reinvented Redis sorted sets.
A Simple mapping that changes how you design systems
| Problem | Typical Solution | Better Fit |
|---|---|---|
| Sessions | DB table | Redis + TTL |
| Rate limiting | DB counters | Redis INCR |
| Leaderboards | SQL sort | Redis Sorted Set |
| Caching | In-memory JS object | Redis (shared) |
What Redis is NOT
- Not your source of truth
- Not your analytics warehouse
- Not a replacement of Postgres
It is the fast lane your system uses when waiting is unacceptable
Question for you (and I’m genuinely curious):
👉 Where would Redis help the most in your current system?
Caching? Sessions? Rate limiting? Something else?
Example 1: Chat System (From Basic → Scalable)
Scenario
You’re building a real-time chat app using:
- Node.js
- Socket.IO
- One server (initially)
Without Redis (Day-0 version)
- Socket.IO keeps:
-
online users
-
typing status
-
active rooms
in server memory
-
Works fine ✅
Until…
Problem appears when you scale
You add:
- multiple Node.js servers
- load balancer
Now:
- User A is connected to Server 1
- User B is connected to Server 2
- Server 1 has no idea what’s happening on Server 2
This breaks:
- online status
- typing indicators
- message broadcast
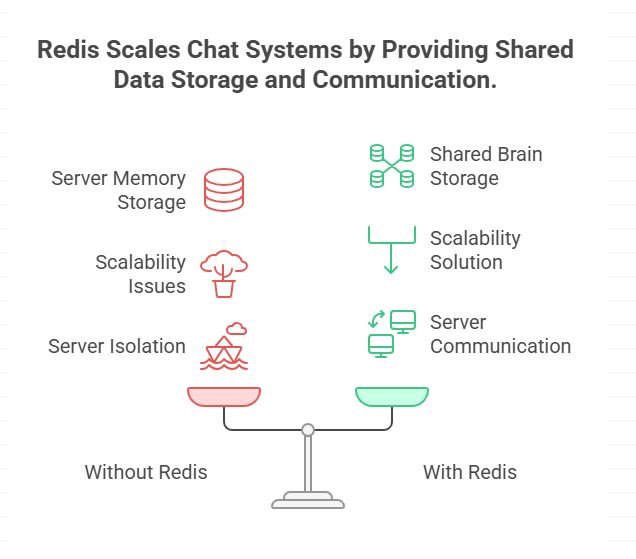
Where Redis fits (Day-1 understanding)
Redis becomes a shared brain for all servers.
What goes into Redis
- Online users →
SET - Typing status →
EXPIRE - Events →
PUB/SUB
Example:
user:123:online -> true (TTL 60s)
chat:room:45 -> publish "user is typing"
Now:
- Any server can know who is online
- Any server can notify others instantly
Important Day-1 takeaway (Chat)
- Redis is not replacing Socket.IO
- Redis is helping Socket.IO scale
Socket.IO handles client communication
Redis handles server-to-server communication
Example 2: SaaS Inventory System (Different Data per User)
Scenario
You have:
- 100s of businesses
- Each has:
- different inventory
- different dashboards
- different permissions
At first glance:
"All users have different data — what will Redis cache?"
Good question 👀
The mistake most developers make
Trying to cache entire dashboards.
That’s expensive ❌
And unnecessary ❌
How Redis is actually useful here
Redis shines at repeated, expensive operations, not raw data.
What you cache (realistic examples)
1. Computed values
total_stock_value:org_42
low_stock_items:org_42
top_selling_items:org_42
These values:
- require joins
- calculations
- aggregations
Compute once → serve fast many times
2. Permission & access checks
user:123:permissions
Avoid hitting DB on every request.
3. Frequently used reference data
- product categories
- warehouse locations
- tax rules
Same across many users.
Memory concern
“Won’t Redis memory explode if we cache per user?”
No — because:
- You don’t cache everything
- You use:
- TTL
- eviction policies
- selective caching
Redis is intentional caching, not a dump.
Day-1 takeaway (SaaS)
Redis helps you:
- reduce DB load
- speed up dashboards
- handle spikes
Even when every user’s data is different.
Common Redis Misconception
“Redis avoids locking” — what it really means
Traditional DB:
- multiple threads
- row locks
- waiting
Redis:
- single-threaded
- commands execute one-by-one
- no waiting for locks
Result:
- predictable latency
- fewer deadlocks
- simpler concurrency model
Summary
Redis isn’t about caching pages.
It’s about removing unnecessary work from your system.
Whether it’s:
- chat events
- inventory calculations
- permission checks
Redis makes your system calmer under load.